Bacterial
Infectious Disease – Bacterial
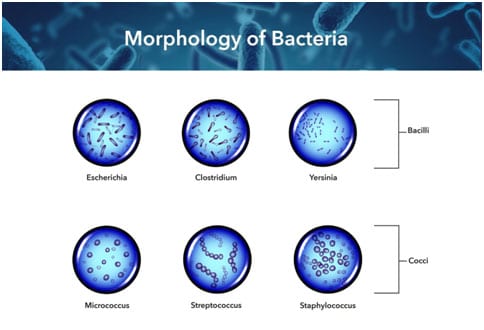
Bacteria are microscopic, single-celled organisms that are found almost everywhere. Broadly speaking, they come in three basic shapes: rods (bacilli), spheres (cocci), or helices (spirilla). In addition to categorization by shape, bacteria may also be classified as gram-positive or gram-negative based on the structure of the bacterial cell wall. While gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer and no outer lipid membrane, gram-negative bacteria have only a thin layer of peptidoglycan and an outer lipid membrane is present.
Although many bacteria are harmless to people, a proportion can cause infection. A bacterial infection is defined as the proliferation of a harmful bacterial strain on or inside the body. Depending on the type of bacterium and the area infected, symptoms may include a fever, chills, lethargy, pain, swelling or redness. More serious cases can lead to sepsis, a potentially fatal condition which arises as bacteria move from the initial site of infection into the bloodstream to cause a massive inflammatory response. If sepsis remains untreated, it can progress into septic shock, a condition which causes low blood pressure and subsequent multi-organ failure.
Many different species of bacteria are capable of infection. Skin infections are typically caused by gram-positive strains of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, whereas foodborne bacterial infections can be attributed to bacteria such as Campylobacter jejuni, Clostridium botulinum, Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella and Vibrio cholerae. Sexually-transmitted bacterial infections include chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis, while other types of bacterial infection are bacterial meningitis, and infections of the respiratory or urinary tracts.
Anti-bacterial antibodies
We offer a wide range of products to support bacterium-based research, including high-quality anti-bacterial antibodies to many of the species mentioned here.